Waveform Plotting Tutorial
Read the files as shown at the Reading Seismograms page. We will use
two different ObsPy Stream objects throughout
this tutorial. The first one, singlechannel, just contains one continuous
Trace and the other one, threechannel,
contains three channels of a seismograph.
>>> from obspy.core import read
>>> singlechannel = read('https://examples.obspy.org/COP.BHZ.DK.2009.050')
>>> print(singlechannel)
1 Trace(s) in Stream:
DK.COP..BHZ | 2009-02-19T00:00:00.025100Z - 2009-02-19T23:59:59.975100Z | 20.0 Hz, 1728000 samples
>>> threechannels = read('https://examples.obspy.org/COP.BHE.DK.2009.050')
>>> threechannels += read('https://examples.obspy.org/COP.BHN.DK.2009.050')
>>> threechannels += read('https://examples.obspy.org/COP.BHZ.DK.2009.050')
>>> print(threechannels)
3 Trace(s) in Stream:
DK.COP..BHE | 2009-02-19T00:00:00.035100Z - 2009-02-19T23:59:59.985100Z | 20.0 Hz, 1728000 samples
DK.COP..BHN | 2009-02-19T00:00:00.025100Z - 2009-02-19T23:59:59.975100Z | 20.0 Hz, 1728000 samples
DK.COP..BHZ | 2009-02-19T00:00:00.025100Z - 2009-02-19T23:59:59.975100Z | 20.0 Hz, 1728000 samples
Basic Plotting
Using the plot() method of the
Stream objects will show the plot. The default
size of the plots is 800x250 pixel. Use the size attribute to adjust it to
your needs.
>>> singlechannel.plot()
Customized Plots
This example shows the options to adjust the color of the graph, the number of
ticks shown, their format and rotation and how to set the start and end time of
the plot. Please see the documentation of method
plot() for more details on all parameters.
>>> dt = singlechannel[0].stats.starttime
>>> singlechannel.plot(color='red', tick_rotation=5, tick_format='%I:%M %p',
... starttime=dt + 60*60, endtime=dt + 60*60 + 120)
Saving Plot to File
Plots may be saved into the file system by the outfile parameter. The
format is determined automatically from the filename. Supported file formats
depend on your matplotlib backend. Most backends support png, pdf, ps, eps and
svg.
>>> singlechannel.plot(outfile='singlechannel.png')
Plotting multiple Channels
If the Stream object contains more than one
Trace, each Trace will be plotted in a subplot.
The start- and endtime of each trace will be the same and the range on the
y-axis will also be identical on each trace. Each additional subplot will add
250 pixel to the height of the resulting plot. The size attribute is used
in the following example to change the overall size of the plot.
>>> threechannels.plot(size=(800, 600))
Creating a One-Day Plot
A day plot of a Trace object may be plotted by
setting the type parameter to 'dayplot':
>>> singlechannel.plot(type='dayplot')
Event information can be included in the plot as well (experimental feature, syntax might change):
>>> from obspy import read
>>> st = read("https://examples.obspy.org/GR.BFO..LHZ.2012.108")
>>> st.filter("lowpass", freq=0.1, corners=2)
>>> st.plot(type="dayplot", interval=60, right_vertical_labels=False,
... vertical_scaling_range=5e3, one_tick_per_line=True,
... color=['k', 'r', 'b', 'g'], show_y_UTC_label=False,
... events={'min_magnitude': 6.5})
Plotting a Record Section
A record section can be plotted from a Stream object
by setting parameter type to 'section':
>>> stream.plot(type='section')
To plot a record section the ObsPy header trace.stats.distance (Offset) must be
defined in meters. Or a geographical location trace.stats.coordinates.latitude &
trace.stats.coordinates.longitude must be defined if the section is plotted in
great circle distances (dist_degree=True) along with parameter ev_coord.
For further information please see plot()
(Source code, png)
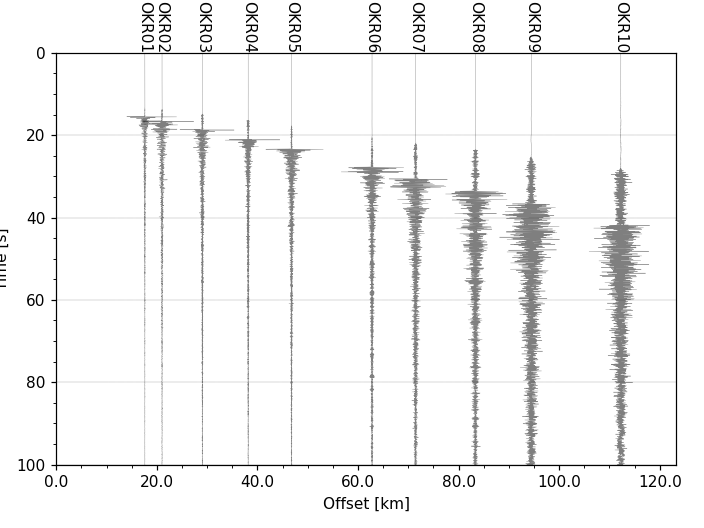
Plot & Color Options
Various options are available to change the appearance of the waveform plot.
Please see plot() method for all possible
options.
Custom Plotting using Matplotlib
Custom plots can be done using matplotlib, like shown in this minimalistic example (see http://matplotlib.org/gallery.html for more advanced plotting examples):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from obspy import read
st = read()
tr = st[0]
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(tr.times("matplotlib"), tr.data, "b-")
ax.xaxis_date()
fig.autofmt_xdate()
plt.show()
(Source code, png)