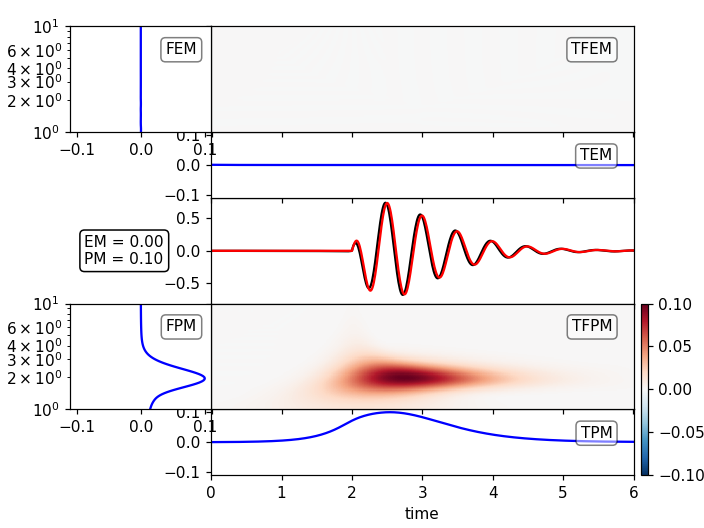
obspy.signal.tf_misfit.plot_tf_misfits
- plot_tf_misfits(st1, st2, dt=0.01, t0=0.0, fmin=1.0, fmax=10.0, nf=100, w0=6, norm='global', st2_isref=True, left=0.1, bottom=0.1, h_1=0.2, h_2=0.125, h_3=0.2, w_1=0.2, w_2=0.6, w_cb=0.01, d_cb=0.0, show=True, plot_args=['k', 'r', 'b'], ylim=0.0, clim=0.0, cmap=<matplotlib.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap object>)[source]
Plot all time frequency misfits and the time series in one plot (per component).
- Parameters
st1 – signal 1 of two signals to compare, type numpy.ndarray with shape (number of components, number of time samples) or (number of timesamples, ) for single component data
st2 – signal 2 of two signals to compare, type and shape as st1
dt – time step between two samples in st1 and st2
t0 – starting time for plotting
fmin – minimal frequency to be analyzed
fmax – maximal frequency to be analyzed
nf – number of frequencies (will be chosen with logarithmic spacing)
w0 – parameter for the wavelet, tradeoff between time and frequency resolution
norm – ‘global’ or ‘local’ normalization of the misfit
st2_isref (bool) – True if st2 is a reference signal, False if none is a reference
left – plot distance from the left of the figure
bottom – plot distance from the bottom of the figure
h_1 – height of the signal axes
h_2 – height of the TEM and TPM axes
h_3 – height of the TFEM and TFPM axes
w_1 – width of the FEM and FPM axes
w_2 – width of the TFEM, TFPM, signal etc. axes
w_cb – width of the colorbar axes
d_cb – distance of the colorbar axes to the other axes
show – show figure or return
plot_args – list of plot arguments passed to the signal 1/2 and TEM/TPM/FEM/FPM plots
ylim – limits in misfit for TEM/TPM/FEM/FPM
clim – limits of the colorbars
cmap – colormap for TFEM/TFPM, either a string or matplotlib.cm.Colormap instance
- Returns
If show is False, returns a matplotlib.pyplot.figure object (single component data) or a list of figure objects (multi component data)
Example
For a signal with pure phase error
See also
[Kristekova2006], Fig.(4)
>>> import numpy as np >>> from scipy.signal import hilbert >>> tmax = 6. >>> dt = 0.01 >>> npts = int(tmax / dt + 1) >>> t = np.linspace(0., tmax, npts) >>> A1 = 4. >>> t1 = 2. >>> f1 = 2. >>> phi1 = 0. >>> phase_shift = 0.1 >>> H1 = (np.sign(t - t1) + 1)/ 2 >>> st1 = (A1 * (t - t1) * np.exp(-2*(t - t1)) * ... np.cos(2. * np.pi * f1 * (t - t1) + phi1 * np.pi) * H1) >>> # Reference signal >>> st2 = st1.copy() >>> # Distorted signal: >>> # generate analytical signal (hilbert transform) and add phase shift >>> st1 = hilbert(st1) >>> st1 = np.real(np.abs(st1) * np.exp((np.angle(st1) + ... phase_shift * np.pi) * 1j)) >>> plot_tf_misfits(st1, st2, dt=dt, fmin=1., fmax=10.)
(Source code, png)